In the vast expanse of the internet, where information reigns supreme, Google's search engine stands as the undisputed gateway to knowledge. Behind the scenes, a complex web of algorithms tirelessly works to provide users with the most relevant and valuable results. This blog aims to unravel the intricate tapestry of Google's Core Algorithms, delving into their fascinating history and tracing their evolution from inception to the latest updates.
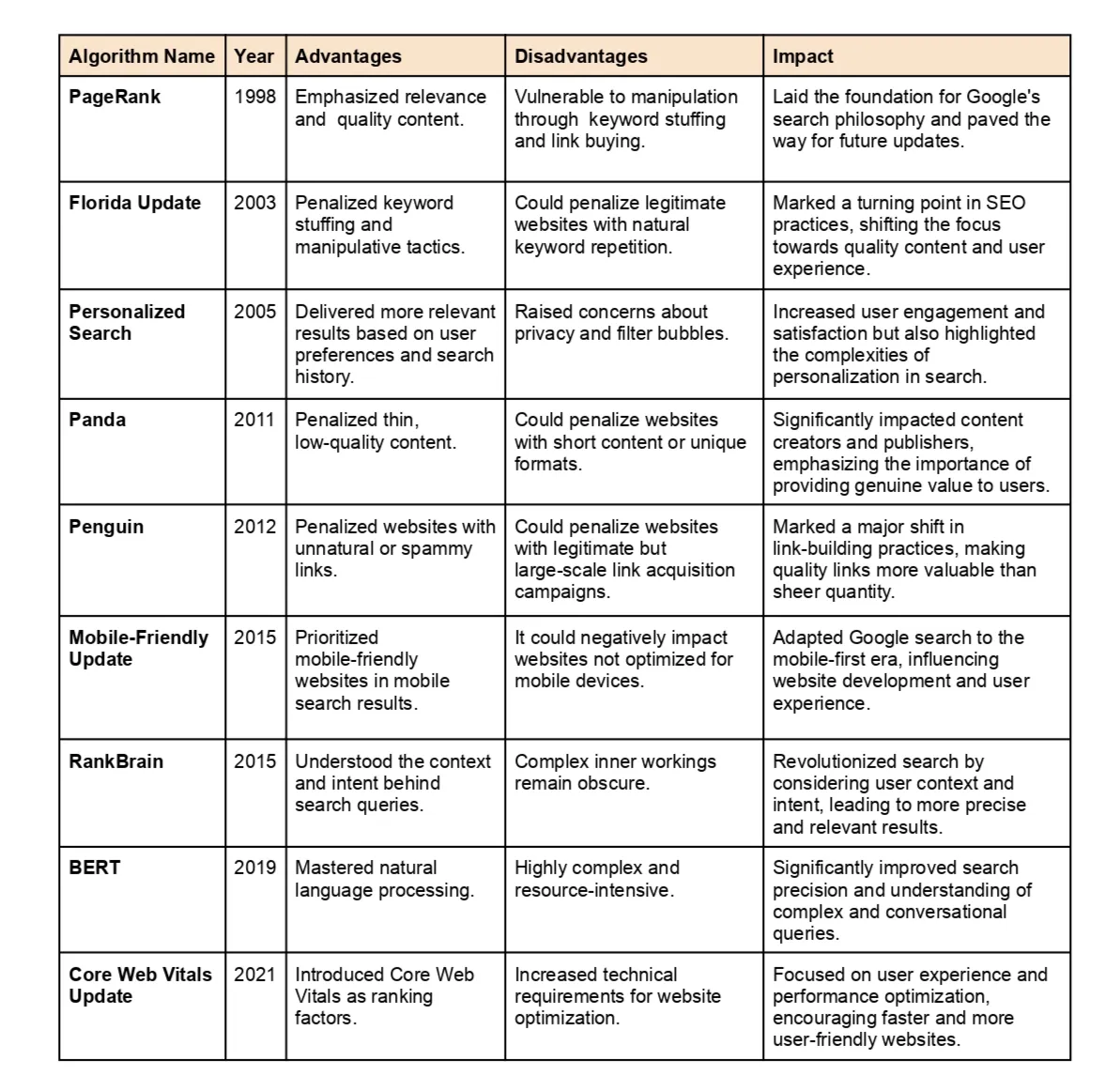
1998: The Genesis: PageRank Algorithm
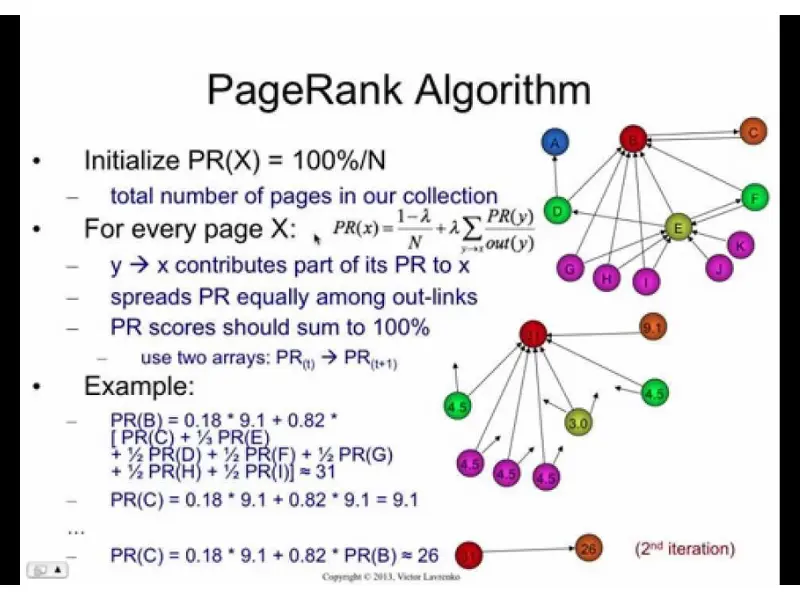
In 1998, Google changed the internet by creating the PageRank algorithm. Larry Page and Sergey Brin created it, and it fundamentally altered how we search the internet. PageRank looked at both the number and quality of links to a page, not just how many links there were. This new way of ranking pages has made search results more accurate and useful. Google focused on links from authoritative and relevant sources, making sure that the most important pages showed up first. PageRank was a big part of Google becoming the top search engine, and it shaped how we find information on the internet.
Example:
Website A has numerous high-quality backlinks from reputable sources, indicating authority and relevance. As a result, it ranks higher in search engine results.
The following video provides more details:
 PageRank algorithm: how it works
PageRank algorithm: how it works
2003: The Florida Update: A Turning Point for SEO
In 2003, the Florida update brought about a big change in how websites tried to be more visible on search engines like Google. Before this update, some websites were using tricks like stuffing keywords everywhere to rank higher. But with Florida, Google started penalizing those tactics, pushing websites to focus on creating good and relevant content for users. This shift not only made the internet better for users but also made SEO (Search Engine Optimization) more ethical. The Florida update played a key role in shaping how we approach SEO today, emphasizing the importance of providing valuable and relevant content to users.
Example:
Website B, which previously stuffed irrelevant keywords on its pages to manipulate rankings, experienced a significant drop in search rankings after the Florida update. Meanwhile, Website C, focusing on quality content, saw improved visibility.
2005: Personalized Search: A Tailored Experience
In 2005, Google changed how we search by introducing personalized search. This feature used our past searches to show results tailored to our preferences. The goal was to make search results more relevant to each person. However, this raised concerns about privacy and the possibility of being trapped in a bubble of similar information. Despite these worries, Google wanted to give users a more customized and user-friendly search experience. The debate between personalization and privacy became a significant topic, highlighting the ongoing discussion about finding a balance between personalized services and safeguarding individual user information in the ever-changing world of digital information.
Example:
Users searching for both "apple" (the fruit) and "Apple" (the tech company) could see personalized results based on their past searches, potentially limiting exposure to diverse perspectives on the term "apple."
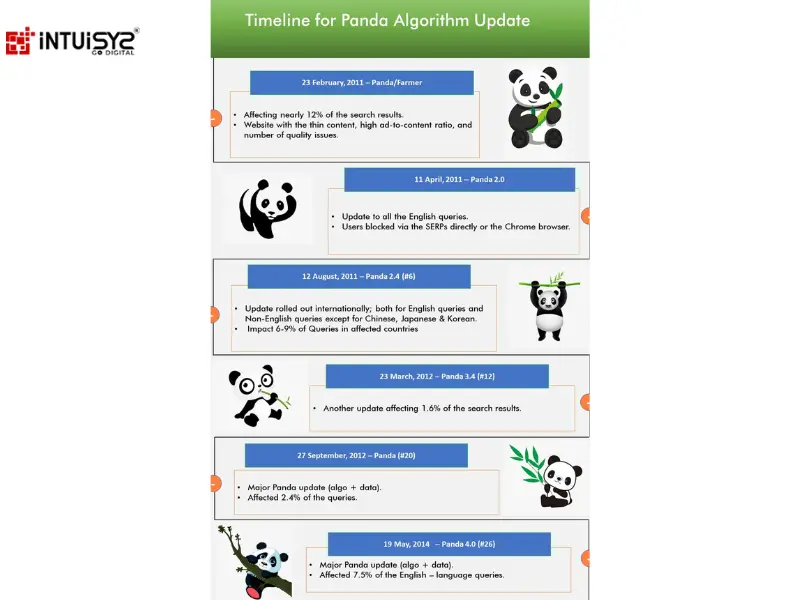
2011: Panda Algorithm: Quality Content Triumphs
In 2011, Google changed how websites were ranked with the Panda update. It was like a quality check, targeting sites with poorly written or repetitive content. If a website didn't have good quality content, it would be ranked lower in search results. This was a big deal because it shifted the focus from having a lot of content to having good content. Businesses and website owners had to change their approach, putting more effort into creating helpful and meaningful content for users. Panda showed everyone that having high-quality content was the key to getting noticed online, emphasizing that quality is more important than quantity when it comes to showing up in search results.
Example:
Website D, known for producing thin and repetitive content, was heavily penalized by Panda. In contrast, Website E gained visibility with in-depth and informative content.
2012: Penguin Algorithm: Taming Unnatural Links
In 2012, a big change happened in the SEO world with the Penguin algorithm. This algorithm tackled the problem of websites using manipulative practices to build links, like creating unnatural or spammy links. Penguin penalized such websites, pushing for a change towards more natural and authentic ways of building links. The update highlighted that having quality links which are relevant and authentic is more important than just having a lot of links. By penalizing websites trying to cheat the system with fake links, Penguin aimed to ensure that search results truly reflected the value of genuine content. This shift encouraged website owners and SEO experts to focus on building high-quality, contextually relevant links, promoting a more trustworthy and user-friendly approach to link-building in the ever-changing world of search engine optimization.
Example:
Website F, which relied on purchasing spammy links, faced penalties and a drop in rankings. Website G, with a natural and organic link-building strategy, gained search visibility.
2015: Mobilegeddon: Embracing Mobile-Friendly Websites
In 2015, Google made a big change to how it ranks websites with the Mobile-Friendly Update, also known as "Mobilegeddon." This update was a response to the growing use of smartphones, emphasizing the increasing importance of mobile devices. Mobilegeddon gave priority to websites that were easy to use on mobile phones in mobile search results. On the flip side, it penalized websites that were not well-optimized for smaller screens and touchscreens. The goal was to make sure that mobile users had a better experience by showing them websites that worked well on their devices. This was a significant moment for businesses and website owners, as they had to focus on making their websites mobile-friendly to stay visible and accessible. Mobilegeddon highlighted how crucial it is for websites to be compatible with mobile devices, considering the changing preferences and habits of users in a world that's increasingly centered around mobile technology.
Example:
Website H, optimized for mobile devices with responsive design and fast load times, saw increased visibility in mobile search results. The website I, lacking mobile optimization, experienced a decline.
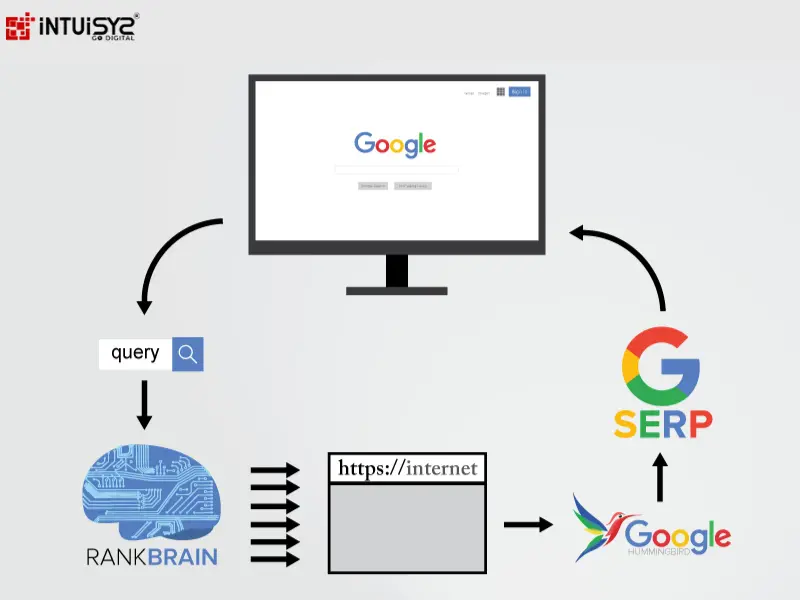
2015: RankBrain: The Era of Machine Learning
In 2015, Google introduced RankBrain, a game-changer that brought machine learning into its core algorithm. This was a big deal in the world of artificial intelligence. RankBrain used advanced machine learning to figure out the context and intent behind search queries. Unlike older algorithms, RankBrain could learn from how users behaved and adapt to give more relevant search results. This was a major step forward for Google in making search results better. RankBrain brought a level of understanding of what users really wanted that traditional algorithms couldn't achieve. By using machine learning in RankBrain, Google showed its commitment to using cutting-edge technologies. This move reinforced Google's position as a leader in search engines, always working to improve how precise and relevant their search results are.
Example:
When users search for the term "Java," RankBrain considers context and intent, providing results based on the user's likely interest, whether it's related to programming, coffee, or an island.
2019: BERT Algorithm: Mastering Natural Language Processing
In 2019, there was a big change in how we search online, and it's called BERT. BERT is like a super-smart way for computers to understand what we're looking for. Unlike the old systems that only focused on single words, BERT looks at the whole conversation. It's like talking to someone who understands not just individual words but how everything fits together. BERT does the same with our search questions, making Google really good at understanding what we mean, even if we use complicated or casual language. It's like Google is becoming an expert reader, making our searches more accurate and helpful. This is just the beginning of a cool journey in making computers truly understand the power of language.
Example:
A user's query, "2019 Brazil traveller to the USA needs a visa," is better understood by BERT, recognizing the importance of the preposition "to" in determining the user's intent.
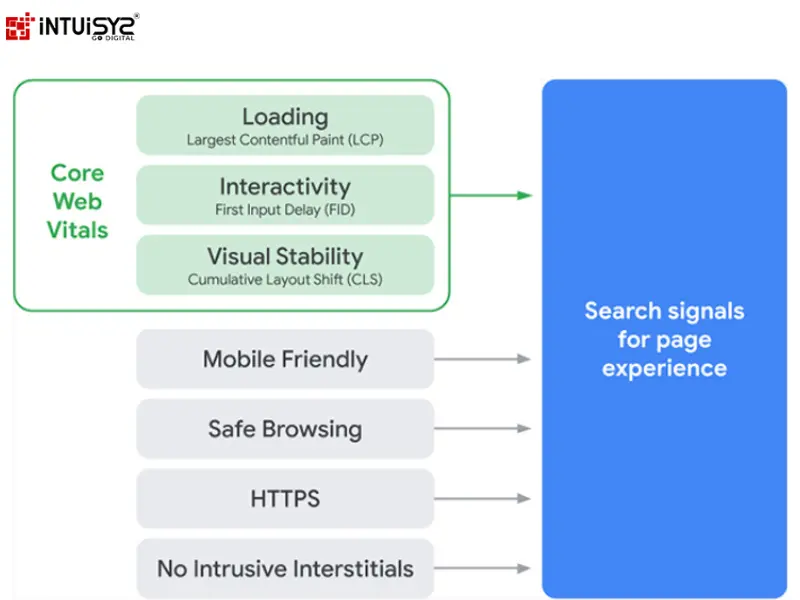
2021: Core Web Vitals and Page Experience Update
In 2021, Google made a big change in how it ranks websites with the Page Experience Update. This update looked at Core Web Vitals, which are important factors like how fast a page loads, how interactive it is, and how visually stable it is. These factors help measure the overall experience users have on a website. The update highlighted how crucial it is for websites to provide a smooth and user-friendly browsing experience to show up higher in search results. Websites that focused on making their pages load quickly, work well, and remain visually stable were rewarded with better rankings. The Page Experience Update showed that Google cares about making users happy by encouraging website owners to create efficient, responsive, and visually stable websites, aligning with Google's goal of giving users high-quality and enjoyable online experiences.
Example:
Website J, with fast load times, smooth interactivity, and visual stability, gained an advantage in rankings. Website K, with slow loading times, saw a decline in search visibility.
2024 Google Algorithm Ranking Factors
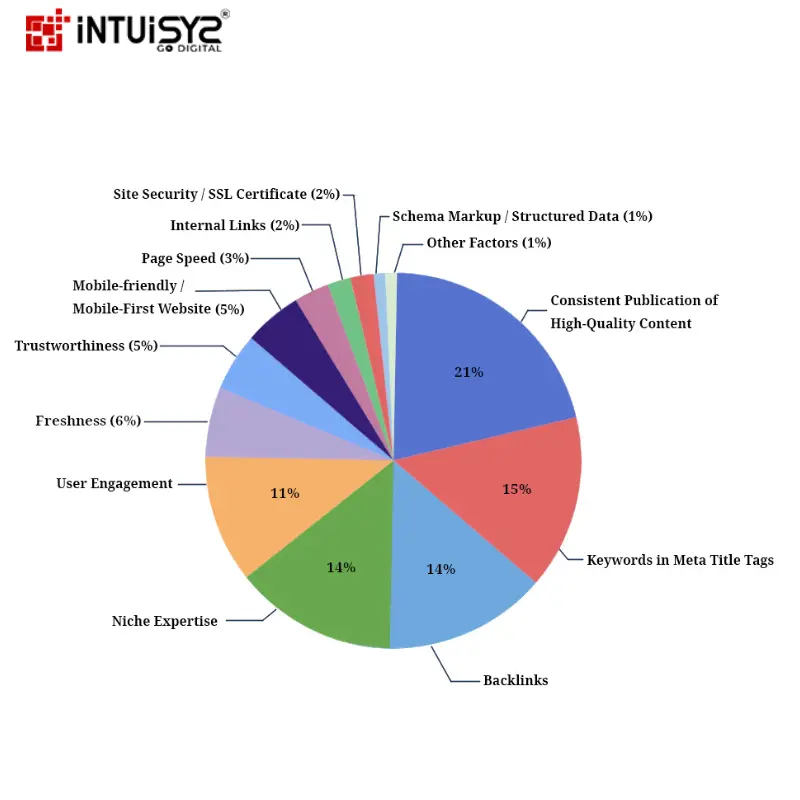
Google's search system is always changing and is like a big, complex creature. It has many small parts and signals that decide what shows up when you search. You can't point to just one main thing because a lot of factors affect what you see in your search results. But here's a simple look at some important parts that affect what you find.
-
Hummingbird: Think of this like a super-smart librarian. It knows what you're looking for in the library and not just the exact words you say. It understands similar words, related ideas, and even the situation you're asking about.
-
RankBrain: Picture this librarian watching how people use the library. They see which books are read all the way through, which ones are quickly looked at, and which ones are left alone. This helps them organize the shelves so you can easily find the most helpful and interesting books.
-
Core Updates: Imagine the library getting a makeover from time to time. Google does this to make sure the library is always well-organized and has the best stuff. They clean out old, wrong, or unhelpful things, so you can always find the right and useful information.
Apart from the main librarians, lots of things affect your search adventure. How well the book is written (using the right words), how much other people like the book and talk about it (links), and even how easy it is to read and use (how fast it loads and works on a phone) are all important.
In simple words, Google wants to be the best helper in your research. It's always getting smarter to lead you to the most helpful stuff online. Just make sure your website has really good, interesting, and easy-to-find information, and Google will put it at the top.
Conclusion
Google's core algorithms have undergone a remarkable evolution, shaping the landscape of online search. From the revolutionary PageRank to the latest updates like Core Web Vitals, each algorithm reflects Google's commitment to relevance, quality, and user experience. As the digital realm evolves, so does Google, continually striving to be the ultimate guide in the vast realm of online knowledge.

